Security with SSL Certificates
Making the web safer.
The certificate
SSL certificates provide end to end encryption for data sent to and from a website.
The basic idea dates back to the nineties, when programmers became concerned that data could be intercepted by a third party; potentially, that meant hackers could sit between the website and the visitor, watching all of the information that went back and forth. On eCommerce sites, that would mean that they'd gain access to email addresses and payment details. Clearly this was unacceptable: a solution was needed.
SSL encryption was added to websites to ensure that all data was made secure. They are installed directly onto the server and ensure that any information sent by your site, or by your site's visitors can not be intercepted. As all data is fully encrypted, anyone who did get to look at it couldn't decipher its meaning.
This is why they're such a good idea.
They make your site safe and protect the customer - perfect!
Google and SSLs
In 2016, we made a point of highlighting a few changes that Google were making to Merchant Center. In essence, they were rejecting products from websites without an SSL certificate.
No certificate, no Merchant Center.
![]()
It was a simple change that had some fairly major effects. Still, it was nothing new. Since 2014, Google have been recommending that you have an SSL certificate. In fact, Google explicitly say that they use it as a ranking signal; having one improves your Google ranking!
For Google, it's all part of making the web a safer place.
Chrome 56 and Firefox 51
Google's Chrome is the most popular browser in the world. That means that more visitors to your site use Chrome than any other.
That's why we take notice when they make major changes.
From February 2017, Chrome is going to be flagging more sites as insecure.
From the end of January with Chrome 56, Chrome will mark HTTP sites that collect passwords or credit cards as non-secure. Enabling HTTPS on your whole site is important, but if your site collects passwords, payment info, or any other personal information, it's critical to use HTTPS. Without HTTPS, bad actors can steal this confidential data. #NoHacked
This is great; it protects the visitor and encourages them to use your website. This is what to look out for:
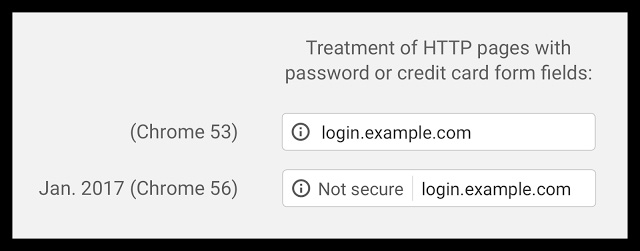
That 'Not Secure' wording will show on any page that records visitor information, if it is outside the protection of an SSL. Simply put: Your need an SSL Certificate!
Chrome have said that in future they're going to expand their warnings, so it's essential that you get one sorted. It protects your customers, improves their experience and boosts your SEO ranking. There is no reason not to!
Now, just to reinforce the point, since the last version of Firefox was released, you can see identical warnings there, too! They're not as big as Chrome, but they're still bigger than anyone else.
Taken together, Chrome and Firefox account for 75% of all internet traffic.
That means that if you don't currently have an SSL certificate, please contact us, and we will be happy to set one up for you!
We have been able to implement new ways to support our customers' preferred journeys in selecting our kind of products with ease.
Brian Hume, Martec International
Get in Touch